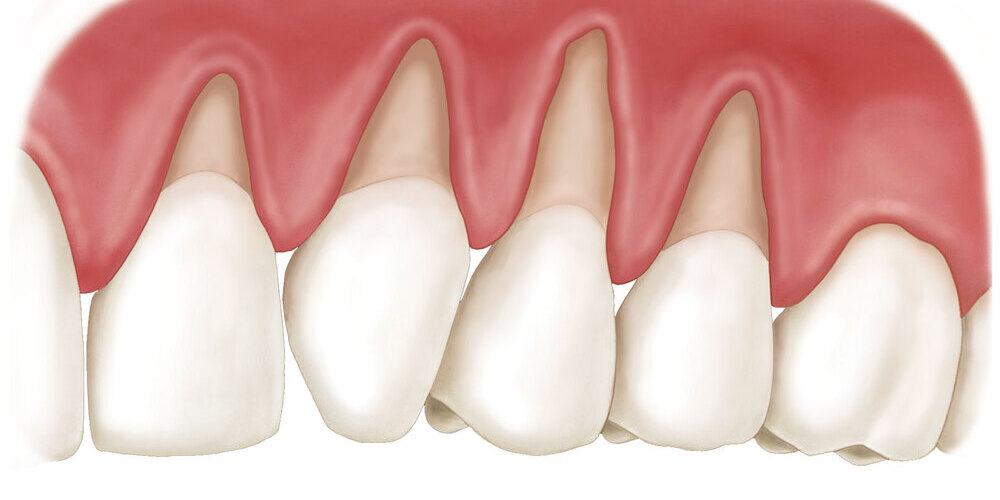
What Causes Gum Recession?
What is Gum Recession?
Gum recession is a type of gum disease. This occurs when your gum tissue pulls away from your teeth, exposing the underlying roots. This makes your teeth more vulnerable to decay. Your teeth may become more sensitive when brushing or eating. Gum recession can be mild, moderate, or severe and can affect one or multiple teeth.
Gum recession can be mild, moderate, or severe and can affect one or multiple teeth. The severity of gum recession is often categorized as follows:
- Mild Recession: This stage involves minimal exposure of the tooth root. You might notice slight sensitivity when brushing or eating hot, cold, or sweet foods.
- Moderate Recession: At this level, a more noticeable portion of the tooth root is exposed. Sensitivity can become more pronounced, and you may experience discomfort during daily oral hygiene routines.
- Severe Recession: Severe gum recession exposes a significant portion of the tooth root, leading to heightened sensitivity and an increased risk of decay and infection. This stage often requires professional dental intervention.
It’s important to understand that gum recession can target specific teeth or groups of teeth. Common scenarios include:
- Localized Recession: Affects one or a few teeth, typically where aggressive brushing or localized periodontal disease has occurred.
- Generalized Recession: Involves multiple teeth across different areas of the mouth, often linked to systemic factors such as genetic predisposition or widespread periodontal disease.
Understanding the extent and pattern of your gum recession can help in tailoring an effective treatment plan with your dental care provider.
Who Does Gum Recession Affect?
While gum recession can affect people of all ages, it is most commonly seen in individuals over the age of 65. You are more likely to experience gum recession if:
- You have periodontal disease
- You have had braces or other orthodontic treatment
- You use chewing tobacco
- You have a lip or tongue piercing
- You brush your teeth aggressively
How Common is Gum Recession?
Gum recession is a common dental problem. In fact, about 88% of people over the age of 65 have gum recession in one or more teeth.
Symptoms and Causes
What are the Symptoms of Gum Recession?
The most noticeable symptom of gum recession is the exposure of the tooth root. Other warning signs include:
- Pain or discomfort near your gum line
- Sensitivity to heat, cold, and sweets
- Sensitivity when brushing and flossing your teeth
- Sensitivity during dental cleanings
If left untreated, gum recession can lead to bone loss, tooth mobility or looseness, and even tooth loss. If you notice any of these symptoms, you should see a dentist immediately.
What Causes Gum Recession?
Your gums can recede for various reasons. The causes of gum recession include:
- Brushing your teeth too hard or aggressively
- Plaque or tartar buildup
- Periodontal disease
- Trauma or injury to your gum tissue
- Abnormal tooth positioning (misalignment)
- Smoking, using e-cigarettes, or chewing tobacco
- Lip and tongue piercings
Often poor oral hygiene can contribute to gum recession, but this isn’t always the case. Many people have a genetic predisposition to thin gum tissue. Regardless of the cause, timely diagnosis and treatment can help prevent long-term oral health issues.
Diagnosis and Tests
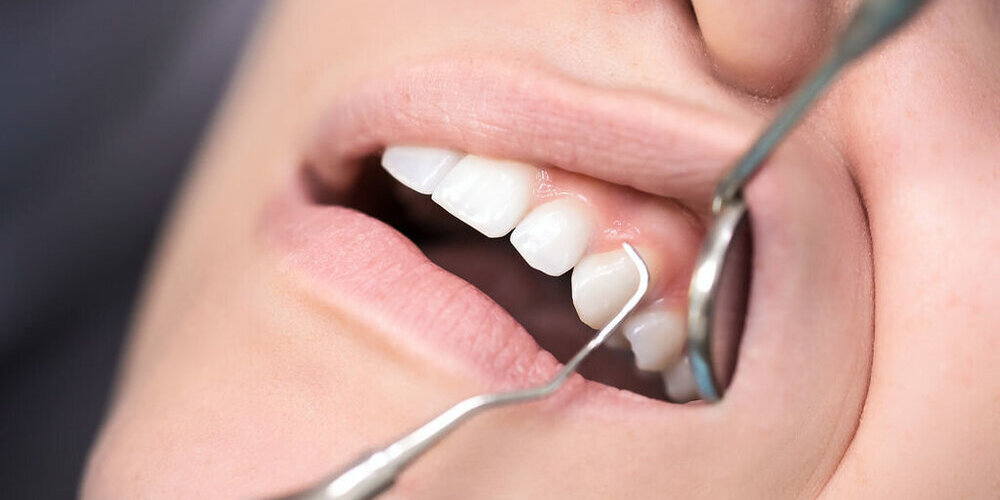
How is Gum Recession Diagnosed?
Your dentist can diagnose gum recession during a routine examination. Using a special tool called a periodontal probe, the amount of gum recession on each tooth is measured. Bone loss is often seen in areas of recession. Therefore, your dentist will measure the periodontal pockets around each tooth. Healthy pockets range from 1 to 3 mm in size. In gingivitis, pockets are 4 mm in size. If you have periodontal disease, your pockets will be 5 mm or more. A dental X-ray may also be taken to assess the extent of bone loss. This helps determine the severity of the gum recession and guides the treatment plan. Regular dental check-ups are crucial in detecting gum recession early on, as prompt intervention can prevent further damage and help preserve your oral health.
Management and Treatment
Can Gums Grow Back?
Unfortunately, receded gums do not grow back. However, you can take necessary steps to prevent further worsening of gum recession. Proper oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing and flossing, can help maintain gum health and prevent the progression of gum recession. In some cases, your dentist may recommend a deep cleaning procedure called scaling and root planing to remove plaque and tartar buildup below the gumline. This helps promote gum reattachment and prevents further recession. In more severe cases, surgical treatments like gum grafting may be necessary to cover exposed tooth roots and restore gum tissue.
How Can I Reduce Sensitivity Caused by Gum Recession?
Many people with gum recession experience pain or sensitivity. This is because your tooth roots are not covered by the protective layer of enamel. Your dentist may apply fluoride varnish or other desensitizing agents to reduce discomfort associated with gum recession. You can also use desensitizing toothpaste at home. Your dentist may use anesthetic agents during your dental cleaning to make you more comfortable.
What is the Best Toothpaste for Gum Recession?
Desensitizing toothpaste can help alleviate discomfort associated with gum recession. Active ingredients like potassium nitrate, stannous fluoride, arginine, and strontium chloride are helpful for reducing sensitivity. These components help calm the nerves inside your teeth. It is best to use desensitizing toothpaste over a long period, as it may take several weeks to start working.
How is Gum Recession Treated?
The treatment for gum recession largely depends on what’s causing it. Mild cases of gum recession can be improved with non-surgical treatments such as topical antibiotics, fillings, or orthodontics. However, in most cases, a gum surgery procedure will be necessary to fully correct the issue.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Non-surgical treatments for gum recession may include:
Scaling and Root Planing
If gum recession is caused by periodontal disease, your dentist will work with you on improving your oral hygiene. Scaling and root planing (curettage) can be performed under local anesthesia to remove harmful bacteria located deep within the gum line that cause periodontal disease.
Dental Fillings
In cases of sensitivity due to gum recession, composite fillings in tooth color can be used to camouflage the receding teeth. This helps cover the exposed tooth root, making the area less noticeable and more comfortable.
Orthodontics
Crooked, tilted, or rotated teeth can cause gum recession. In such cases, braces may be an option. Once the tooth is properly aligned, the gum level may improve over time.
Surgical Treatments
Gum Surgeries
Gum surgery is the most predictable and long-lasting treatment option for gum recession. Typically, this procedure is performed by a periodontist (gum specialist).
During this surgery, a gum graft is used to replace your missing gum tissue. The graft is usually taken from your palate. The gum graft is placed and stitched in the area where the recession is significant. Free gingival graft (FGG) is a commonly used and predictable surgical method, especially to increase the amount of attached gingiva. Along with increasing the amount of attached gingiva with FGG, it is also possible to achieve root coverage to some extent.
How Long Does It Take to Recover From Free Gingival Graft Surgery?
Your recovery time will depend on various factors such as how many teeth were treated, where the gum graft came from, and what type of grafting procedure was done. In most cases, people who undergo gum recession surgery feel back to normal within about two weeks. Your surgeon will give you detailed post-operative instructions. You should closely follow these instructions to ensure a comfortable and successful recovery.
Prevention
Can I Prevent Gum Recession?
Recession cannot always be prevented, especially if you are genetically predisposed to having thin gum tissue. However, by following proper gum recession care instructions, you can significantly reduce your risk. Some ways to prevent gum recession include:
- Gently brushing your teeth with a soft-bristled brush.
- Using dental floss and other interproximal cleaners to remove plaque between your teeth.
- Using dental floss and other interproximal cleaners to remove plaque between your teeth.
- Eating a healthy, balanced diet.
- Scheduling regular check-ups and dental cleaning appointments with your dentist.
- If you have any questions about your oral hygiene, do not hesitate to consult your dentist. Remember that many people suffer from gum recession, and it is a treatable condition.
When Should I See My Gum Specialist?
If you notice that your tooth roots are more visible than before or if your tooth sensitivity has increased, it may be gum recession. It’s important to contact your dentist or periodontist at the first sign. The earlier gum recession is detected and treated, the better your chances of achieving optimal oral health.
What Questions Should I Ask My Gum Specialist?
Learning everything you can about gum recession can help you avoid common problems and regain your oral health. If you have questions, we welcome you to visit FineUp Clinic.
- How advanced is my gum recession?
- Are there non-surgical options that might work for me?
- What is the likelihood of my gum recession returning?
- How often should I get my teeth cleaned?
If left untreated, gum recession can harm your oral health. If you have complaints such as bleeding gums, receding gums, pain, or sensitivity in your teeth, you should see a dentist without delay. Even if pain or sensitivity does not develop, you should still see a dentist if there is gum recession. They can explain how serious the issue is and what steps you can take to protect your oral health.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What Causes Gum Recession?
Your gums can recede for various reasons. The causes of gum recession may include periodontal disease, genetics, aggressive tooth brushing, insufficient dental care, hormonal changes, tobacco use, teeth grinding or clenching, misaligned teeth, and oral piercings.
Who Does Gum Recession Affect?
While gum recession can affect people of all ages, it is most common in adults over the age of 40. However, it can also occur in teenagers and children due to genetic predisposition or poor oral hygiene habits.
How Common is Gum Recession?
Gum recession is a common dental problem. In fact, about 88% of people have at least one area of mild gum recession by the age of 65.
What are the Symptoms of Gum Recession?
The most noticeable symptom of gum recession is the exposure of the tooth roots. Other symptoms may include tooth sensitivity, longer-looking teeth, visible notches on the teeth near the gumline, and changes in tooth position or bite.
How is Gum Recession Diagnosed?
Your dentist can diagnose gum recession during a routine examination by measuring the depth of the gum tissue surrounding each tooth and checking for exposed tooth roots.
Can Gums Grow Back?
Unfortunately, receded gums do not grow back. However, you can undergo treatments to prevent further recession and protect the exposed tooth roots.
